在爬虫的过程中如何使用Redis的Bloomfilter去重
时间:2024/11/12作者:未知来源:手揣网教程人气:
- [摘要]本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于如何使用Redis的Bloomfilter去重,既用上了Bloomfilter的海量去重能力,又用上了Redis的可持久化能力,有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一...
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于如何使用Redis的Bloomfilter去重,既用上了Bloomfilter的海量去重能力,又用上了Redis的可持久化能力,有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
前言:
“去重”是日常工作中会经常用到的一项技能,在爬虫领域更是常用,并且规模一般都比较大。去重需要考虑两个点:去重的数据量、去重速度。为了保持较快的去重速度,一般选择在内存中进行去重。
数据量不大时,可以直接放在内存里面进行去重,例如python可以使用set()进行去重。
当去重数据需要持久化时可以使用redis的set数据结构。
当数据量再大一点时,可以用不同的加密算法先将长字符串压缩成 16/32/40 个字符,再使用上面两种方法去重;
当数据量达到亿(甚至十亿、百亿)数量级时,内存有限,必须用“位”来去重,才能够满足需求。Bloomfilter就是将去重对象映射到几个内存“位”,通过几个位的 0/1值来判断一个对象是否已经存在。
然而Bloomfilter运行在一台机器的内存上,不方便持久化(机器down掉就什么都没啦),也不方便分布式爬虫的统一去重。如果可以在Redis上申请内存进行Bloomfilter,以上两个问题就都能解决了。
代码:
# encoding=utf-8import redisfrom hashlib import md5class SimpleHash(object): def __init__(self, cap, seed): self.cap = cap self.seed = seed def hash(self, value): ret = 0 for i in range(len(value)): ret += self.seed * ret + ord(value[i]) return (self.cap - 1) & retclass BloomFilter(object): def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=6379, db=0, blockNum=1, key='bloomfilter'): """ :param host: the host of Redis :param port: the port of Redis :param db: witch db in Redis :param blockNum: one blockNum for about 90,000,000; if you have more strings for filtering, increase it. :param key: the key's name in Redis """ self.server = redis.Redis(host=host, port=port, db=db) self.bit_size = 1 << 31 # Redis的String类型最大容量为512M,现使用256M self.seeds = [5, 7, 11, 13, 31, 37, 61] self.key = key self.blockNum = blockNum self.hashfunc = [] for seed in self.seeds: self.hashfunc.append(SimpleHash(self.bit_size, seed)) def isContains(self, str_input): if not str_input: return False m5 = md5() m5.update(str_input) str_input = m5.hexdigest() ret = True name = self.key + str(int(str_input[0:2], 16) % self.blockNum) for f in self.hashfunc: loc = f.hash(str_input) ret = ret & self.server.getbit(name, loc) return ret def insert(self, str_input): m5 = md5() m5.update(str_input) str_input = m5.hexdigest() name = self.key + str(int(str_input[0:2], 16) % self.blockNum) for f in self.hashfunc: loc = f.hash(str_input) self.server.setbit(name, loc, 1)if __name__ == '__main__':""" 第一次运行时会显示 not exists!,之后再运行会显示 exists! """ bf = BloomFilter() if bf.isContains('http://www.baidu.com'): # 判断字符串是否存在 print 'exists!' else: print 'not exists!' bf.insert('http://www.baidu.com')说明:
Bloomfilter算法如何使用位去重,这个百度上有很多解释。简单点说就是有几个seeds,现在申请一段内存空间,一个seed可以和字符串哈希映射到这段内存上的一个位,几个位都为1即表示该字符串已经存在。插入的时候也是,将映射出的几个位都置为1。
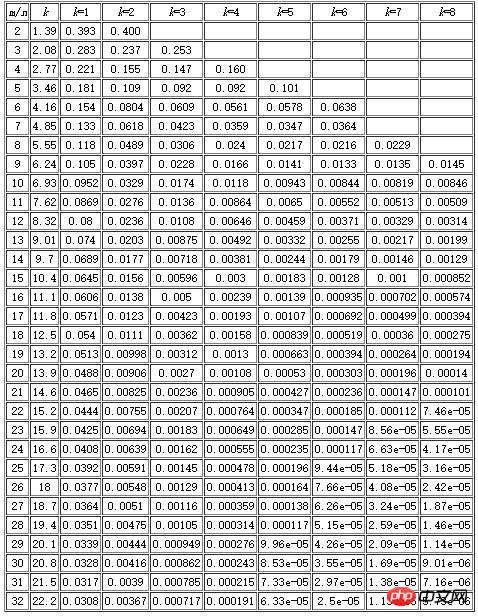
需要提醒一下的是Bloomfilter算法会有漏失概率,即不存在的字符串有一定概率被误判为已经存在。这个概率的大小与seeds的数量、申请的内存大小、去重对象的数量有关。下面有一张表,m表示内存大小(多少个位),n表示去重对象的数量,k表示seed的个数。例如我代码中申请了256M,即1<<31(m=2^31,约21.5亿),seed设置了7个。看k=7那一列,当漏失率为8.56e-05时,m/n值为23。所以n = 21.5/23 = 0.93(亿),表示漏失概率为8.56e-05时,256M内存可满足0.93亿条字符串的去重。同理当漏失率为0.000112时,256M内存可满足0.98亿条字符串的去重。
基于Redis的Bloomfilter去重,其实就是利用了Redis的String数据结构,但Redis一个String最大只能512M,所以如果去重的数据量大,需要申请多个去重块(代码中blockNum即表示去重块的数量)。
代码中使用了MD5加密压缩,将字符串压缩到了32个字符(也可用hashlib.sha1()压缩成40个字符)。它有两个作用,一是Bloomfilter对一个很长的字符串哈希映射的时候会出错,经常误判为已存在,压缩后就不再有这个问题;二是压缩后的字符为 0~f 共16中可能,我截取了前两个字符,再根据blockNum将字符串指定到不同的去重块进行去重。
总结:
基于Redis的Bloomfilter去重,既用上了Bloomfilter的海量去重能力,又用上了Redis的可持久化能力,基于Redis也方便分布式机器的去重。在使用的过程中,要预算好待去重的数据量,则根据上面的表,适当地调整seed的数量和blockNum数量(seed越少肯定去重速度越快,但漏失率越大)。
以上就是在爬虫的过程中如何使用Redis的Bloomfilter去重的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
网站建设是一个广义的术语,涵盖了许多不同的技能和学科中所使用的生产和维护的网站。
关键词:在爬虫的过程中如何运用Redis的Bloomfilter去重